Natural borneol enhances bisdemethoxycurcumin-induced cell cycle arrest in the G2/M phase through up-regulation of intracellular ROS in HepG2 cells
Abstract
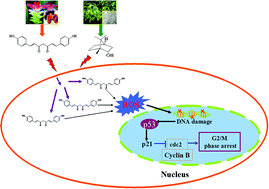
Bisdemethoxycurcumin (BDCur) has been found widely in foods such as cheese, butter, etc., and in curry (powder) as a spice. It has been reported to possess anticancer activity. However, its poor absorption limited its application. Natural borneol (NB) has been used as a promoter of drug absorption and widely used in candies, beverages, baked goods, chewing gum and other foods. Thus, we investigated whether NB could potentiate the cellular uptake of BDCur, and elucidated the molecular mechanisms of their combined inhibitory effects on HepG2 cells. Our results demonstrate that NB significantly enhanced the cellular uptake of BDCur. Induction of cell cycle arrest in HepG2 cells by NB and BDCur in combination was evidenced by accumulation of the G2/M cell population. Further investigation on the molecular mechanism showed that NB and BDCur in combination resulted in a significant decrease in the expression level of Cdc2 and cyclin B. Moreover, studies also found that ROS acted as an upstream mediator in NB/BDCur-induced HepG2 cell growth inhibition and led to DNA damage with up-regulation of the expression level of phosphorylated ATM and p53. Our findings suggest that the strategy of using NB and BDCur in combination may have promising potential applications in cancer chemoprevention.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...