Saponarin from barley sprouts inhibits NF-κB and MAPK on LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells†
Abstract
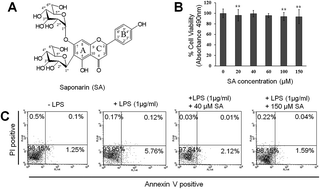
Saponarin (SA), a natural flavonoid, is known for its antioxidant and hepatoprotective activities. SA is the predominant compound (1142.7 ± 0.9 mg per 100 g) in barley sprouts, constituting 72% of the total polyphenol content. We investigated, for the first time, the effects of SA from barley sprouts on cellular anti-inflammatory responses. In lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages, SA suppressed the activation of NF-κB, as evidenced by the inhibition of NF-κB DNA binding, nuclear translocation, IκBα phosphorylation, and reporter gene expression, and it downregulated the expression of the pro-inflammatory mediator IL-6. Furthermore, SA reduced the transcription of NF-κB target molecules COX2 and FLIP inhibited the phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinases ERK and p38. These results suggest that SA isolated from barley sprouts exerts anti-inflammatory effects in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 macrophages via inhibition of NF-κB, ERK and p38 signaling. Thus, SA may be a promising natural anti-inflammatory agent.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...