Piceid presents antiproliferative effects in intestinal epithelial Caco-2 cells, effects unrelated to resveratrol release
Abstract
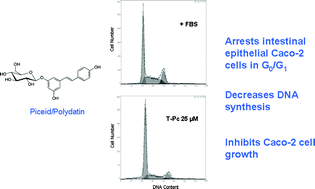
Trans-piceid (T-Pc) is abundant in Polygonum cuspidatum and in grapes and grape products such as wine. Piceid reaches high levels in the stomach and intestine with rapid oral absorption. Tissues, such as liver tissue, can deglycosylate piceid to release resveratrol, so piceid can be considered a source of resveratrol, which has numerous biological activities such as antiproliferative effects. Therefore, the aim of this work was to analyze the action of T-Pc on intestinal epithelial cell growth. Our results show that T-Pc has antioxidant activity similar to that of trans-resveratrol (T-Rv) and higher than that of Trolox. Moreover, T-Pc (1–50 μM) inhibited Caco-2 cell growth and DNA synthesis in a concentration-dependent manner. We observed an increase in the percentage of cells in G0/G1 phase induced by T-Pc and the induction of apoptosis. Furthermore, we observed that Caco-2 cells did not have β-glucosidase activity and that Caco-2 cell cultures did not significantly deglycosylate T-Pc in our experimental conditions. On the basis of our results we propose, for the first time, that T-Pc must not be considered exclusively as a T-Rv source, and presents antiproliferative effects on intestinal epithelial cells through the modulation of the cell cycle and apoptosis by itself. Moreover, a synergistic action of T-Pc and T-Rv can be considered.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...