Effect of porous starch concentrations on the microbiological characteristics of microencapsulated Lactobacillus acidophilus
Abstract
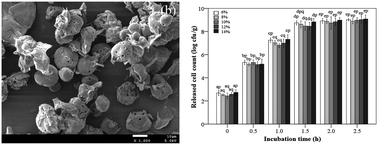
This study was conducted to evaluate the effect of different porous starch concentrations on the microbiological characteristics of microencapsulated Lactobacillus acidophilus. Results showed that the encapsulation efficiency of L. acidophilus with porous starch at a concentration of 10% is the highest (61.2%) compared with other concentrations. The morphology of microencapsulation was observed by scanning electron microscope. Moreover, survival assays at pH 1.5 indicated that, at the end of 3 h, the cell numbers for microencapsulation with 10% porous starch and free cells showed 2.63 and 4.01 logarithmic cycle reductions, respectively. However, no significant reduction in viable count was observed in microcapsules as well as for free cells at pH 6.5 for 3 h. The improving survival rate under high temperatures was observed with increasing concentration of porous starch from 6 to 10% and decreasing temperature. The released counts were increased with prolonged incubation time and were between 6.34 and 6.46 log CFU g−1 at the end of storage exposure for 2.5 h to simulated colonic pH solution. These results indicated that porous starch with the optimum concentration as a carrier can be considered as an innovative technology to improve the stability of L. acidophilus.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...