Inhibition of dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) by tryptophan containing dipeptides
Abstract
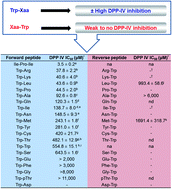
Twenty seven Trp containing dipeptides were evaluated for their ability to inhibit dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV), a key enzyme involved in incretin hormone processing. Novel DPP-IV inhibitors were identified comprising of three potent dipeptides (Trp-Arg, Trp-Lys and Trp-Leu) with half maximum inhibitory concentration (IC50 values) <45 μM. With the exception of Leu-Trp which was ∼20 times less potent than Trp-Leu, their reverse peptide did not inhibit DPP-IV. Trp-Asp was the only peptide studied herein with an N terminal Trp residue which was not a DPP-IV inhibitor. Phosphorylation resulted in an increase in DPP-IV IC50, giving values of 482.1 ± 12.9 and >11 000 μM for Trp-Thr and Trp-pThr, respectively. The mode of inhibition of these peptides was studied using Lineweaver and Burk kinetic analysis, which showed both competitive and non-competitive modes of inhibition depending on the peptide sequence. This suggested binding of the peptide inhibitors to different locations on DPP-IV. In silico analysis of the milk proteome revealed that some of the DPP-IV inhibitors identified herein may be released from milk proteins following enzymatic digestion. The results are relevant to understanding the mechanism(s) involved in DPP-IV inhibition by short peptides. This in turn may dictate a more targeted approach for the release of potent peptides from milk proteins with the view of developing biofunctional hydrolysates for the management of type 2 diabetes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...