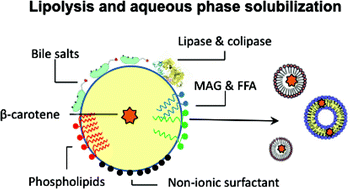
The influence of interfacial structure and lipid physical state on colloidal stability and digestibility of solid lipid nanoparticle dispersions (SLN) and canola oil-in-water emulsions (COE) stabilized with the non-ionic surfactants Poloxamer 188 (P188) and Tween 20 (T20) were examined and the release of encapsulated β-carotene (BC) under simulated gastrointestinal conditions determined. While the SLN and COE were all stable during exposure to gastric conditions (mean diameter ∼115 nm), more destabilization was observed for the COE than SLN during the duodenal phase. ζ-Potential measurements indicated rapid adsorption of bile salts (BS) and phospholipids (PL) to both solid and liquid interfaces, with greater surfactant displacement observed for the COE. Compared to the SLN, significantly more lipolysis and BC transfer to the aqueous phase was observed for both the COE-P188 and COE-T20 (p < 0.05). The properties of the colloidal structures present in the aqueous phase, which are important in terms of the uptake of lipolytic products and lipophilic bioactives, depended on non-ionic surfactant type, the extent of lipid digestion, as well as the presence of BS and PL.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...