Effect of various electrolytes and other wastewater constituents on the degradation of volatile organic compounds in aqueous solution by pulsed power plasma technology†
Abstract
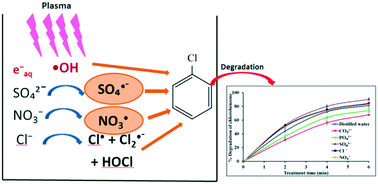
A gas phase discharge pulsed plasma approach was employed to evaluate the effect of different electrolytes (anions such as CO32−, PO43−, SO42−, Cl− and NO3−) on the degradation of chlorobenzene. Plasma degradation of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) such as chloroform, chlorobenzene, toluene and MIBK (methyl isobutyl ketone) in the presence of various wastewater matrices such as sulfate ion, organic matter and turbidity was studied. An initial concentration of 200 mg L−1 of each of the VOCs and an input voltage of 17 kV were used. The highest degradation of chlorobenzene was obtained in the presence of SO42− ions and lowest when CO32− was present in solution. The increase in chlorobenzene removal efficiency in the presence of SO42− could be due to the formation of SO4˙− radicals during plasma discharge. The ˙OH radical concentration decreased from 194 to 106.7 μM when sulfate was increased from 0 to 83.75 mM. This may be due to the reaction of ˙OH with sulfate ions to form SO4˙− radicals during plasma discharge. By employing tert-butyl alcohol (TBA) as a selective ˙OH scavenger, the role of SO4˙− radicals in chlorobenzene degradation was elucidated. A significant positive effect of sulfate on chloroform degradation was also observed. Organic matter and turbidity did not show a major effect on the degradation of selected VOCs. The turbidity of solutions decreased significantly after 10 min of plasma treatment. The results of the study clearly indicate the effectiveness of pulsed power plasma technology for the treatment of industrial wastewaters.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...