Oily bilge water treatment using DC/AC powered electrocoagulation†
Abstract
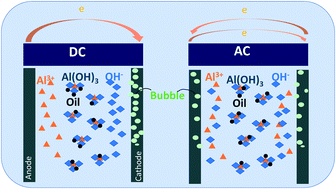
Bilge water is a complex oily wastewater that may contain a variety of contaminants and salts. Electrocoagulation (EC) recently emerged as an efficient process for bilge water treatment, but its energy cost and lifespan are primary challenges. This study compared the oil removal and energy consumption of both DC and AC powered EC units and investigated the effects of salinity for the first time. Different current densities, voltages, and operation modes (constant current and constant voltage) were investigated to understand the electrochemical kinetics of high salinity bilge water. Results showed that both DC and AC power sources satisfied the oil reduction requirement with over 99% oil removal and a high current density was found to be more efficient in oil removal. High salinity (e.g. 35 g L−1) could slightly improve demulsification during electrocoagulation by reducing the zeta potential. Different frequencies (0.25, 0.5 and 1 Hz) of AC power were applied to EC units and it was found that a low frequency was more efficient for oil removal. The results also showed that a constant AC was more efficient in maintaining the same performance with a less energy cost increment than the DC mode.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
