Detection, identification and control of polar iodinated disinfection byproducts in chlor(am)inated secondary wastewater effluents†
Abstract
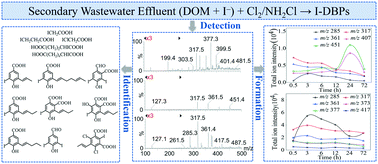
Disinfection of wastewater effluents could generate numerous toxic disinfection byproducts (DBPs) during wastewater reclamation owing to the complexity of their dissolved organic matter. Recently, iodinated disinfection byproducts (I-DBPs) have attracted increasing attention as a result of their higher toxicity than their brominated and chlorinated analogues. In this study, various new polar I-DBPs in chlor(am)inated wastewater effluents were detected with ultra-performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry (UPLC/ESI-tqMS) by setting a precursor ion scan of m/z 126.9. Three new polar I-DBPs were identified as wastewater I-DBPs, including iodoacetic acid, chloroiodoacetic acid and 3,5-diiodo-4-hydroxybenzaldehyde. The remaining new polar I-DBPs were proposed with structures, nine of which were found to be aromatic halogenated DBPs, and six of which were proposed to be in a group because they share closely related m/z values, retention times, and fragmentation pathways. In addition, formation of these new polar I-DBPs with disinfectants and contact times was also studied. Compared with chlorination, chloramination generated more species and higher concentrations of new polar I-DBPs. Furthermore, control of the newly detected polar I-DBPs during chlorination by coagulation, resin adsorption, and combined processes was compared. Resin adsorption showed a higher precursor removal efficiency than coagulation, and thus achieved a better control of these new polar I-DBPs. Coagulation followed by resin adsorption was the most effective compared with single coagulation and single resin adsorption.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...