Dissolved oxygen and nitrate effects on the reduction and removal of divalent mercury by pumice supported nanoscale zero-valent iron†
Abstract
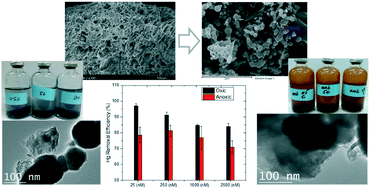
A series of batch experiments were conducted to identify the effects of dissolved oxygen (DO) and nitrate on the removal and reduction of Hg(II) by a pumice supported nanoscale zero-valent iron (p-nZVI) composite. After the adsorption and consecutive reduction of Hg(II) in an anoxic solution, zero-valent iron, and ferrous and ferric irons were found on the surface of the p-nZVI with a chain-like structure; while in the oxic solution, a thick ferric shell was found on the surface of the p-nZVI with collapsed chain structures. In Hg(II) sorption isotherm tests, with 25, 250, 1000, and 2500 nM of Hg(II), the Hg(II) sorption capacity of the p-nZVI was 6.1 mg g−1 in the oxic aqueous solution and 1.5 mg g−1 in the anoxic aqueous solution. While the adsorption of Hg(II) was more favorable in the presence of DO, the headspace Hg(0), as well as dissolved Fe(II), was largely increased in the absence of DO. The removal of Hg(II) in oxic and anoxic suspensions was not affected by nitrate levels ranging from 0.08 to 8 mM. In contrast, Hg(0) concentration in headspace increased with an increase of nitrate, which was related to the enhanced dissolved Fe(II) production. The experimental results of this study suggest that the absence of DO and the presence of nitrate in groundwater could significantly increase Hg(0) in groundwater and adjacent atmosphere during the usual remediation process using relevant nZVI techniques. The effective capture and treatment methods of Hg(0) should be developed for better application of p-nZVI-based technologies.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...