Optimizing the performance of a membrane bio-electrochemical reactor using an anion exchange membrane for wastewater treatment
Abstract
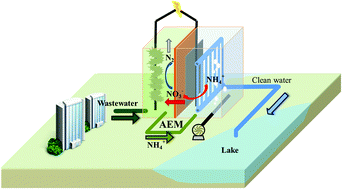
A membrane bioelectrochemical reactor (MBER) is a system integrating ultrafiltration membranes into microbial fuel cells (MFCs) for energy-efficient wastewater treatment. To improve nitrogen removal, an MBER based on an anion exchange membrane (AEM), the MBER-A, was investigated for treating synthetic solution or actual wastewater during a 200-day operation. The MBER-A significantly improved the removal of total nitrogen to 56.9% with the synthetic solution, compared with 7.6% achieved in the MBER containing a cation exchange membrane (MBER-C). This was mainly due to the removal of nitrate through both nitrate migration across AEM and heterotrophic denitrification in the anode. The final filtrate from MBER-A contains 11.9 mg L−1 nitrate-nitrogen, 6.0 mg L−1 nitrite-nitrogen, and less than 1 mg L−1 ammonia-nitrogen. The MBER-A achieved 91.3 ± 6.4% of COD removal, resulting in a COD concentration of 21.6 ± 17.8 mg L−1 in its membrane filtrate. The transmembrane pressure (TMP) remained below 10 kPa when being operated with synthetic solution. The actual wastewater (primary effluent) led to the decrease in both COD and nitrogen removal, likely due to complex composition of organic compounds and low electricity generation. The MBER-A decreased the COD concentration by 84.5 ± 14.4% and total nitrogen concentration by 48.4 ± 1.9%. The ammonia-nitrogen concentration remained at 0.3 mg L−1 in the final filtrate. The energy consumption by the MBER-A could be significantly decreased through reducing the strength of the anolyte recirculation rate. Those results encourage further investigation and development of the MBER technology for energy efficient removal of organic and nitrogen compounds from wastewater.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...