Few-layered tungsten selenide as a co-catalyst for visible-light-driven photocatalytic production of hydrogen peroxide for bacterial inactivation†
Abstract
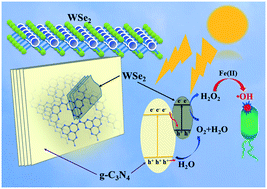
Sustainable and “green” technologies for hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) production have aroused increasing interest, yet challenges prevail in production of H2O2 for environmental applications. In this study, tungsten selenide (WSe2) with a few-layered microstructure was used as a new co-catalyst to synthesize H2O2 under visible light irradiation. The ultrathin WSe2 nanosheets were anchored onto a g-C3N4 surface by in situ growth solvothermal methods. The as-prepared WSe2/g-C3N4 showed remarkably enhanced H2O2 production efficiency without organic electron donors, which was 11.8 times higher than that of pristine g-C3N4. H2O2 was generated via O2 reduction mediated by photogenerated e−, and dissolved O2 could be generated by water oxidation and in situ used to produce H2O2 under anaerobic conditions. The introduction of WSe2 not only promoted visible light absorption, but also facilitated the charge transfer efficiency by forming a Z-scheme rather than a type II heterojunction. The photogenerated e− was enriched onto WSe2, leading to the high H2O2 production activity. Moreover, the in situ generated H2O2 could be directly used for pathogenic bacteria inactivation through Fenton reactions without external H2O2 addition. This work is expected to open an avenue for developing novel photocatalysts towards sustainable H2O2 production for water disinfection and related environmental applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...