Protonation of rhodanine polymers for enhancing the capture and recovery of Ag+ from highly acidic wastewater†
Abstract
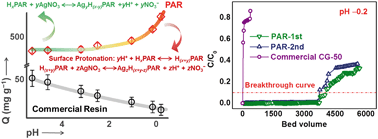
Selective capture and direct recovery of silver ions from highly acidic wastewater are desirable but challenging for sustainable remediation of contamination. In this work, contraposing the characteristics of actual Ag-polluted water, poly-allylrhodanine (PAR) is designed and synthesized as an adsorbent. Different from most reported adsorbents, PAR features a unique acidity-enhanced adsorptivity property, thus achieving an ultrahigh capacity (651.0 mg g−1) and outstanding selectivity (>100) in the capture of Ag+ from wastewater with strong acidity (pH −0.2). Moreover, the purity of the reclaimed Ag+ reaches up to 99.80%, delivering an enormous economic benefit. Further characterization and theoretical calculations uncover that the C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) S and C–S groups on PAR act as adsorption sites to coordinate the Ag+ ions via a special pH-dependent protonation exchange mechanism. In the treatment of actual Ag-polluted water, the treatment capacity of PAR is as high as 4015 bed volumes (BV) per run at pH = −0.2, which is 100-fold higher than that of commercial resin, highlighting its great potential in practical applications. The wastewater feature-directed design concept and the high-performance adsorbent of PAR reported in this work may be helpful to fill the gap between the experimental laboratory and practical remediation of Ag-containing wastewater.
S and C–S groups on PAR act as adsorption sites to coordinate the Ag+ ions via a special pH-dependent protonation exchange mechanism. In the treatment of actual Ag-polluted water, the treatment capacity of PAR is as high as 4015 bed volumes (BV) per run at pH = −0.2, which is 100-fold higher than that of commercial resin, highlighting its great potential in practical applications. The wastewater feature-directed design concept and the high-performance adsorbent of PAR reported in this work may be helpful to fill the gap between the experimental laboratory and practical remediation of Ag-containing wastewater.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Environmental Remediation


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...