Transformation and species identification of CuO nanoparticles in plant cells (Nicotiana tabacum)†
Abstract
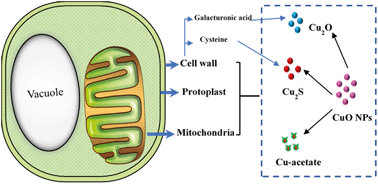
The transformation of CuO nanoparticles (NPs) during interaction with Nicotiana tabacum L. cv. bright yellow-2 (BY-2) cells was investigated in this study. CuO NPs were taken up, and transformed into Cu2O, Cu2S and Cu acetate after incubation with plant cells for 12 h based on high resolution transmission electron microscopy and X-ray absorption near-edge spectroscopy analysis. The transformation of CuO NPs initially occurred on cell walls with Cu2O and Cu2S being the main transformation products. Galacturonic acid as an important component of cell walls was mainly responsible for reducing CuO to Cu2O and cysteine for the formation of Cu2S. Cu2+ ions could not be transformed into any Cu-based particles (CuO, Cu2O, or Cu2S) on cell walls. After internalization, CuO NPs could also be transformed into Cu2O and Cu2S through interacting with protoplasts as well as mitochondria, confirming that CuO NPs were able to transform intracellularly. Moreover, Cu2O NPs showed higher toxicity to plant cells as compared to CuO NPs with similar individual sizes, indicating that the transformation of CuO NPs enhanced their toxicity to plant cells. These findings could provide new insights into better understanding the transformation and fate of metal-based NPs in living organisms and environments.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
