3,4-Hydroxypyridinone-modified carbon quantum dot as a highly sensitive and selective fluorescent probe for the rapid detection of uranyl ions†
Abstract
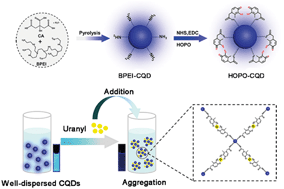
Although a variety of analysis techniques have been established and developed for uranium detection in aqueous solution, there is still an urgent need for a new technique that can be utilized for the on-site and instant monitoring of uranium concentration, particularly during a nuclear accident that requires an ultrafast response. Traditional analysis techniques suffer from the clear demerit of the relatively long time needed for an accurate detection. Herein, we report a solution to this challenge by developing a 3,4-hydroxypyridinone-functionalized carbon quantum dot (HOPO-CQD), which can be used as a fluorescent probe for the almost instant monitoring of uranyl ions. The developed probe exhibited an excellent sensitivity (limit of detection, 6.53 ppb), a high selectivity towards uranyl ions, and an extremely short response time (30 s). The excellent uranyl detection performance of the HOPO-CQDs originated from the strong and specific interaction between the HOPO ligand and the uranyl ion, leading to a unique uranyl-induced aggregation of the carbon quantum dots. This phenomenon is highly selective to uranyl ions and is attractive for further separation applications. This is the first time that post-modified CQDs are employed for the in situ, real-time detection of uranyl ions in aqueous solutions, with a promising potential for practical applications in the near future.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Environmental Remediation


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...