Proteomics and antioxidant enzymes reveal different mechanisms of toxicity induced by ionic and nanoparticulate silver in bacteria†
Abstract
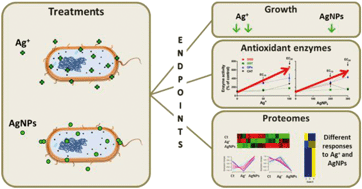
The increased use of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) raises concerns about their impacts on aquatic ecosystems. The impacts of Ag+ and AgNPs were assessed on proteomic and antioxidant enzymatic responses of Pseudomonas sp. M1. The effects of Ag+ on bacterial growth were stronger than those of AgNPs (EC20 = 107.1 μg L−1 for Ag+; EC20 = 307.2 μg L−1 for AgNPs), indicating the lower toxicity of the latter. At EC20, the activities of antioxidant enzymes increased more under exposure to Ag+ than to AgNPs, particularly for superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase (stimulation of 667% and 433%, respectively). A total of 166 proteins were identified by SWATH-MS; among these, only 59 had their content significantly altered by one or both forms of silver. Exposure to AgNPs resulted in an increase of about 54% of these proteins, whereas 54% decreased under exposure to Ag+. Gene Ontology enrichment analysis revealed that protein folding and transmembrane transport were the most relevant processes affected by Ag+ exposure, whereas AgNPs mostly affected translation. Also, results suggest that each form of silver induced different adaptive responses. Furthermore, the low levels of Ag+ released from AgNPs (<0.1%) support a minor role of dissolved silver in AgNP toxicity to Pseudomonas sp. M1.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...