Highly efficient adsorption of uranium(vi) from aqueous solution by a novel adsorbent: titanium phosphate nanotubes†
Abstract
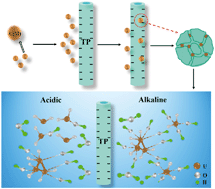
A novel adsorbent, titanium phosphate nanotube, was fabricated through a facile solvothermal method. The adsorbent was characterized by scanning electron microscopy, nitrogen adsorption–desorption isotherms, X-ray diffraction, zeta potential and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy in detail. The as-prepared adsorbent exhibited high performance for U(VI) adsorption from aqueous solution. The influencing factors including pH, temperature, contact time, adsorbent concentration and adsorbate concentration on the U(VI) adsorption were systematically investigated. The sorption of U(VI) on the titanium phosphate nanotube agreed with the Langmuir isotherm model and the maximum adsorption capacity was 344 mg g−1, which is relatively higher than most reported materials in recent years. According to kinetic and thermodynamic studies, the adsorption fitted better with a pseudo-second-order model and it was an endothermic and spontaneous process. The U(VI) adsorption was mostly attributed to electrostatic interaction and surface complexation. In addition, desorption and reusability studies on titanium phosphate nanotubes showed that their adsorption capacity was not significantly decreased after 4 cycles, indicating that they may have a promising potential for industrial removal of radionuclides from aqueous solution.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...