Antimicrobial activity of flame-synthesized nano-TiO2 coatings†
Abstract
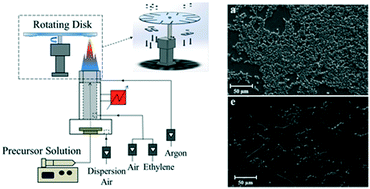
TiO2 in the form of nanocrystals possesses photocatalyst properties leading to excellent capability of degrading a number of environmental contaminants such as organics, bacteria, and viruses. However, the antimicrobial activity of nano-TiO2 coatings against different microorganisms is not yet well established. Candida albicans, Aspergillus niger, Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus mutans are common nosocomial and environmental pathogens responsible for biofilm-associated infections especially in indoor environments. In this study, we produced thin coatings of TiO2 nanoparticles on aluminum substrates and assessed whether they may prevent fungi and bacteria biofilm formation and whether this may be a synergistic effect of TiO2 nanoparticles with UV irradiation, which is more representative of the natural conditions for passive devices. Coatings of flame-synthesized nanoparticles were produced by direct thermophoretic deposition on aluminum substrates through a rotating disk inserted in the flame. Particle and coating characterization was performed by means of differential mobility analysis, Raman and X-ray diffraction spectroscopy. Microbial biofilm formation on substrates with different TiO2 thicknesses were evaluated by the colorimetric crystal violet method and quantified by spectrophotometry in four different fungi and bacteria strains; the results were corroborated by scanning electron microscopy analysis. Substrates with minimal TiO2 nanoparticle layers demonstrated a strong anti-biofilm effect against both fungi and bacteria, due to the well-known cellular component photo-oxidation and to the enhanced nanomaterial surface area. Interestingly, UV irradiation of the substrates at a low intensity for a short time demonstrated a significant enhancement of the titania antimicrobial activity. TiO2 nanoparticle coatings may be proposed as self-cleaning and self-disinfecting materials able to reduce microbial infections, especially in indoor environments where hygiene is needed.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Nanomaterials in air


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...