Nanostructured ZnFeZr oxyhydroxide precipitate as efficient phosphate adsorber in waste water: understanding the role of different material-building-blocks†
Abstract
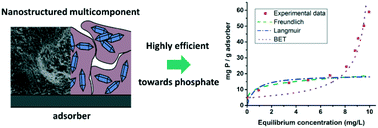
In the recent years great effort has been made to find materials and technologies for removing and recycling phosphate from waste water. We herein present the detailed study on a nanostructured multicomponent material, which turned out to be a very efficient phosphate adsorber. The role of each constituent is carefully examined to understand the collaborative interaction of the components of the nanostructured adsorber. We found evidence that it is particularly the nanostructure of this material, which has a crucial influence on the phosphate adsorption performance, indicating a synergetic effect of the different components. Moreover, the adsorption mechanism was studied dependent on the concentration of phosphate, changing from a Freundlich/Langmuir-like behaviour to a BET-like multilayer adsorption of phosphate on the material. Our work demonstrates that there is high potential for discovering new adsorber materials for environmental applications through careful engineering of the chemical composition in close connection with the materials (nano) structure.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...