Electrochemical DNA sensing strategy based on strengthening electronic conduction and a signal amplifier carrier of nanoAu/MCN composited nanomaterials for sensitive lead detection†
Abstract
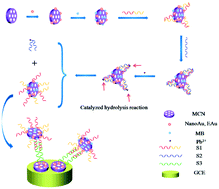
A DNA electrochemical sensor was fabricated using the modification of a glassy carbon electrode (GCE) with ordered mesoporous carbon nitride (MCN), electrodeposited gold nanoparticles (EAu) and methylene blue (MB)/nanoAu/MCN as the signal amplifier, in which MB was inserted into the nanoAu/MCN composites for Pb2+ detection. The secondary structure of the trans-cleaving 8–17 DNAzyme, composed of the substrate strand (S1) and the enzyme strand (S2), was utilized for the sensor fabrication. S1 immobilized on the signal amplifier could hybridize with S2 and form a DNA double helix structure on account of the principle of complementary base pairing. With the activation of Pb2+, S2 was able to cleave the single RNA linkage with S1 by hydrolysis reaction to break S1 into two fragments. One of the fragments NS1′ that was immobilized on the MB/nanoAu/MCN signal amplifier (S1′/MB/nanoAu/MCN) could hybridize with the DNA probe S3 immobilized on the modified electrode. With the help of the MCN’s large specific surface area and the gold nanoparticles’ good charge-transport capacity, the sensor exhibited excellent sensitivity and selectivity. The proposed sensing strategy represented a wide linear response in the range from 1.0 × 10−3 to 1.0 × 10−14 M. The sensor was also tested with real samples and represented a promising method for detecting Pb2+.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...