Comparability of long-term temporal trends of POPs from co-located active and passive air monitoring networks in Europe†
Abstract
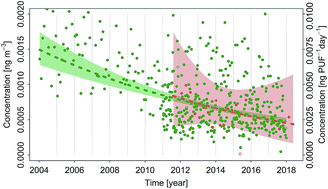
The comparability of data from active (ACT) and passive sampling (PAS) of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) in air is hindered by uncertainties related to the derivation of sampling rates and concentrations, as well as differences in the duration, volume and frequency of sampling. Although data from ACT have been used extensively in short-term PAS calibration studies, no attempts have been made to evaluate the comparability of long-term trends calculated from PAS to established ACT trends. This is crucial, as continuous long-term ACT is unfeasible in most regions of the world. To address these challenges, we calculated and compared trends for organochlorine pesticides (OCPs), polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) and polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs) at the six sites in Europe with at least 5 years of co-located ACT and PAS data (2012–2016): Birkenes, Košetice, Pallas, Råö, Stórhöfði and Zeppelin. Strong agreement of ACT and PAS trends was observed for most OCPs and PCBs. Apart from two PCBs at Stórhöfði, all pairs of ACT and PAS trends followed the same direction. However, differences in the magnitude, significance and confidence intervals of their slopes were observed for some compounds and were primarily attributed to the short duration of the PAS time series. Despite some limitations, our results suggest that the comparability of ACT and PAS POP trends will continue to improve with additional years of data. This study confirms the suitability of PAS for the calculation of long-term POP trends in air, and highlights the importance of continuous sampling at established monitoring sites with consistent analytical methods.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...