The use of the core–shell structure of zero-valent iron nanoparticles (NZVI) for long-term removal of sulphide in sludge during anaerobic digestion†
Abstract
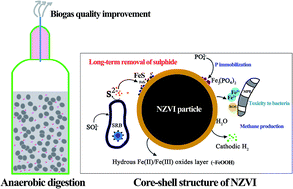
A core–shell structure results in zero-valent iron nanoparticles (NZVI) with manifold functional properties. In this study, the long-term effects of NZVI on hydrogen sulphide removal in an anaerobic sludge digester were investigated. Within 20 days, the average hydrogen sulphide content in the biogas was successfully reduced from 300 (or 3620 of sulphate-rich sludge) mg Nm−3 to 6.1 (121), 0.9 (3.3) and 0.5 (1.3) mg Nm−3 in the presence of 0.05, 0.10 and 0.20% (wt) NZVI, respectively. Methane yield was enhanced at the low NZVI dose (0.05–0.10%) but decreased at the elevated dose (0.20%). Methane production and volatile solid degradation analyses implied that doses of 0.5–0.10% NZVI could accelerate sludge stabilization during anaerobic digestion. The phosphorus fractionation profile suggested that methane production could be inhibited at the elevated NZVI dose, partly due to the limited availability of soluble phosphorus due to the immobilization of bioavailable-P through the formation of vivianite. An analysis of the reducible inorganic sulphur species revealed that the elimination of hydrogen sulphide occurred via the reaction between hydrogen sulphide and the oxide shell of NZVI, which mainly formed FeS and some FeS2 and S0.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...