Biological effects and bioaccumulation of pharmaceutically active compounds in crucian carp caged near the outfall of a sewage treatment plant†
Abstract
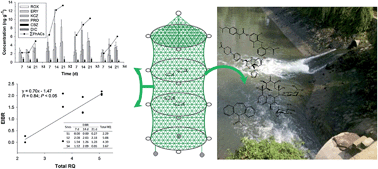
Pharmaceutically active compounds (PhACs) have been universally detected in rivers, lakes and coastal waters that are affected by effluents from sewage treatment plants (STPs). In this study, the biological effects and bioaccumulation of PhACs were assessed in crucian carp (Carassius auratus) caged in an effluent-receiving river for 21 days. Compared with control fish in the laboratory and at a reference site, a significant reduction in hepatosomatic index (HSI) and increase in the biotransformation enzymes ethoxyresorufin O-deethylase (EROD) and glutathione S-transferase (GST) activities were observed in the fish that was caged downstream from the STP outfall. In general, the total concentrations of PhACs detected in fish tissues were in the order as follows: liver > brain > gill > muscle > bile. The bioaccumulation factors (BAFs) for PhACs were between 195 and 2782 in the major storage tissue liver. The corresponding results for both risk quotient (RQ) and enhanced integrated biomarker response (EIBR) based on laboratory and field studies, respectively, indicated that environmental risk for adverse effects to aquatic organisms were clearly higher at the downstream of the STP outfall than at the upstream.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...