Effect of permafrost properties on gas hydrate petroleum system in the Qilian Mountains, Qinghai, Northwest China
Abstract
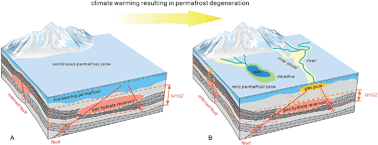
The gas hydrate petroleum system in the permafrost of the Qilian Mountains, which exists as an epigenetic hydrocarbon reservoir above a deep-seated hydrocarbon reservoir, has been dynamic since the end of the Late Pleistocene because of climate change. The permafrost limits the occurrence of gas hydrate reservoirs by changing the pressure–temperature (P–T) conditions, and it affects the migration of the underlying hydrocarbon gas because of its strong sealing ability. In this study, we reconstructed the permafrost structure of the Qilian Mountains using a combination of methods and measured methane permeability in ice-bearing sediment permafrost. A relationship between the ice saturation of permafrost and methane permeability was established, which permitted the quantitative evaluation of the sealing ability of permafrost with regard to methane migration. The test results showed that when ice saturation is >80%, methane gas can be completely sealed within the permafrost. Based on the permafrost properties and genesis of shallow gas, we suggest that a shallow “gas pool” occurred in the gas hydrate petroleum system in the Qilian Mountains. Its formation was related to a metastable gas hydrate reservoir controlled by the P–T conditions, sealing ability of the permafrost, fault system, and climatic warming. From an energy perspective, the increasing volume of the gas pool means that it will likely become a shallow gas resource available for exploitation; however, for the environment, the gas pool is an underground “time bomb” that is a potential source of greenhouse gas.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...