Application of in vivo measurements for the management of cyanobacteria breakthrough into drinking water treatment plants†
Abstract
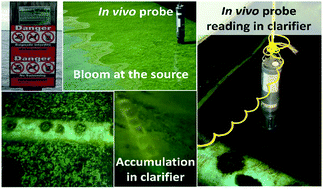
The increasing presence of potentially toxic cyanobacterial blooms in drinking water sources and within drinking water treatment plants (DWTPs) has been reported worldwide. The objectives of this study are to validate the application of in vivo probes for the detection and management of cyanobacteria breakthrough inside DWTPs, and to verify the possibility of treatment adjustment based on intensive real-time monitoring. In vivo phycocyanin YSI probes were used to monitor the fate of cyanobacteria in raw water, clarified water, filtered water, and chlorinated water in a full scale DWTP. Simultaneous samples were also taken for microscopic enumeration. The in vivo probe was successfully used to detect the incoming densities of high cyanobacterial cell number into the clarification process and their breakthrough into the filtered water. In vivo probes were used to trace the increase in floating cells over the clarifier, a robust sign of malfunction of the coagulation–sedimentation process. Pre-emptive treatment adjustments, based on in vivo probe monitoring, resulted in successful removal of cyanobacterial cells. The field results on validation of the probes with cyanobacterial bloom samples showed that the probe responses are highly linear and can be used to trigger alerts to take action.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...