Lipopeptide biosurfactant production bacteria Acinetobacter sp. D3-2 and its biodegradation of crude oil†
Abstract
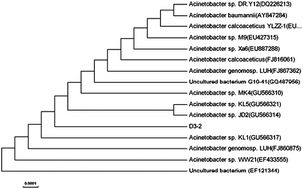
In this work, a hydrocarbon-degrading bacterium D3-2 isolated from petroleum contaminated soil samples was investigated for its potential effect in biodegradation of crude oil. The strain was identified as Acinetobacter sp. D3-2 based on morphological, biochemical and phylogenetic analysis. The optimum environmental conditions for growth of the bacteria were determined to be pH 8.0, with a NaCl concentration of 3.0% (w/v) at 30 °C. Acinetobacter sp. D3-2 could utilize various hydrocarbon substrates as the sole carbon and energy source. From this study, we also found that the strain had the ability to produce biosurfactant, with the production of 0.52 g L−1. The surface tension of the culture broth was decreased from 48.02 to 26.30 mN m−1. The biosurfactant was determined to contain lipopeptide compounds based on laboratory analyses. By carrying out a crude oil degradation assay in an Erlenmeyer flask experiment and analyzing the hydrocarbon removal rate using gas chromatography, we found that Acinetobacter sp. D3-2 could grow at 30 °C in 3% NaCl solution with a preferable ability to degrade 82% hydrocarbons, showing that bioremediation does occur and plays a profound role during the oil reparation process.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...