Aggregation behavior of nanodiamonds and their functionalized analogs in an aqueous environment
Abstract
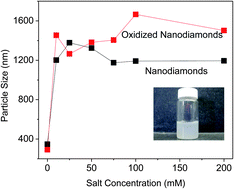
The colloidal behavior of aqueous dispersions of detonation nanodiamonds (DNDs) and carboxylated nanodiamonds (DND-COOH) which were synthesized via a microwave process is presented. Both forms of DNDs were found to be relatively stable in aqueous solutions, but aggregated rapidly in the presence of mono and divalent salts. The critical coagulation concentration (CCC) values for DNDs and DND-COOH were estimated to be between 8 and 10 mM for NaCl and 7 and 8 mM for MgCl2. In general, the formation of carboxyl groups on the DND surface did not alter colloidal behavior as dramatically as it is known to do for other nanocarbons especially carbon nanotubes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...