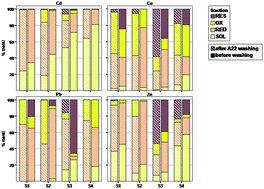
Accumulation of metals in soil at elevated concentrations causes risks to the environmental quality and human health for more than one hundred million people globally. The rate of metal release and the alteration of metal distribution in soil phases after soil washing with a sulfosuccinamate surfactant solution (Aerosol 22) were evaluated for four contaminated soils. Furthermore, a sequential extraction scheme was carried out using selective extractants (HAcO, NH2OH·HCl, H2O2 + NH4AcO) to evaluate which metal species are extracted by A22 and the alteration in metal distribution upon surfactant-washing. Efficiency of A22 to remove metals varied among soils. The washing treatment released up to 50% of Cd, 40% of Cu, 20% of Pb and 12% of Zn, mainly from the soluble and reducible soil fractions, therefore, greatly reducing the fraction of metals readily available in soil. Metal speciation analysis for the solutions collected upon soil washing with Aerosol 22 further confirmed these results. Copper and lead in solution were mostly present as soluble complexes, while Cd and Zn were present as free ions. Besides, redistribution of metals in soil was observed upon washing. The ratios of Zn strongly retained in the soil matrix and Cd complexed with organic ligands increased. Lead was mobilized to more weakly retained forms, which indicates a high bioavailability of the remaining Pb in soil after washing. Comprehensive knowledge on chemical forms of metals present in soil allows a feasible assessment of the environmental impact of metals for a given scenario, as well as possible alteration of environmental conditions, and a valuable prediction for potential leaching and groundwater contamination.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...