Proton-coupled electron transfer of tyrosines in Photosystem II and model systems for artificial photosynthesis: the role of a redox-active link between catalyst and photosensitizer
Abstract
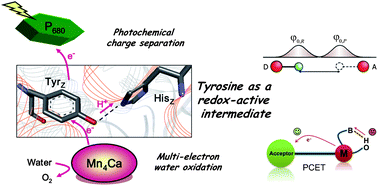
- This article is part of the themed collection: Biomimetic approaches to artificial photosynthesis

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...