Homo- and hetero-dinuclear Pt(ii)/Pd(ii) complexes: studies of hydrolysis, nucleophilic substitution reactions, DNA/BSA interactions, DFT calculations, molecular docking and cytotoxic activity†
Abstract
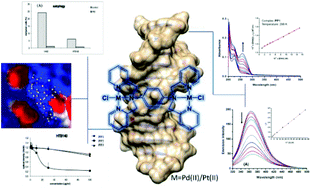
Three dinuclear complexes [Pd2(tpbd)Cl2]Cl2 (PP1), [Pt2(tpbd)Cl2]Cl2 (PP2) and [PdPt(tpbd)Cl2]Cl2 (PP3) (tpbd = N,N,N′,N′-tetrakis(2-pyridylmethyl)benzene-1,4-diamine) have been synthesized and characterized and the protonation constants of their corresponding diaqua analogues have been determined. Also, in water solution, the aqua analogues of these complexes exist as mono-hydroxo, di-hydroxo and dimer μ-hydroxo complexes in the pH between 3.0 and 11.0. Substitution reactions with sulfur- and nitrogen-donor nucleophiles, such as thiourea (Tu), L-methionine (L-Met), glutathione (GSH) and guanosine-5′-monophosphate (5′-GMP), were studied at pH 7.2 by conventional and stopped-flow UV-Vis spectrophotometry and the observed reactivity follows the order: Tu > L-Met > GSH > 5′-GMP. Also, the interactions with calf thymus DNA (CT-DNA) and bovine serum albumin (BSA) were investigated. Competitive studies with DNA were performed in the presence of ethidium bromide and Hoechst dye 33258 as well. The complexes possess the strong ability to react with CT-DNA exhibiting intercalation and more preferable minor groove binding. Nevertheless, all complexes showed a good binding affinity toward BSA with relatively high binding constants. The nature of the binding forces between complexes and biomolecules has been identified as hydrophobic. Experimental results were compared with the molecular docking results, while the relative stability and thermodynamic properties of dinuclear complexes were compared with their mononuclear units by DFT calculations. Among three tested complexes, PP2 showed the most powerful cytotoxic effect on HTB140 and H460 cancer cell lines after 48 h of treatment and exerted a strong long-term influence on the proliferation potential of both tested cell lines. PP2 induced the inhibition of autophagy, G2/M cell cycle arrest and mitotic catastrophe.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...