A simple chemical solution synthesis of nanowire-assembled hierarchical CuO microspheres with enhanced photochemical properties†
Abstract
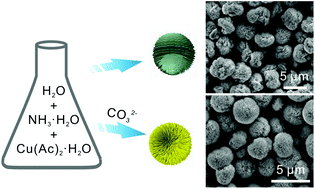
Hierarchical micro/nanostructures manifest attractive prospects for photocatalytic application. Nevertheless, large-scale hierarchical micro/nanostructures for industrial application with facile, low-cost and eco-friendly routes remain difficult. Herein, nanowire-assembled hierarchical CuO microspheres (HCMAW) are synthesized for the first time by CO32− ions induced synthesis route. The time-dependent SEM images reveal that the growth mechanism for HCMAW is the well-known Ostwald ripening with self-assembly. The specific surface area of the HCMAW is 7.265 m2 g−1, which is higher than that of hierarchical CuO microspheres assembled with nanosheets (HCMAS) (4.952 m2 g−1) prepared by direct self-assembly scheme without the introduction of CO32− ions. Meanwhile, the HCMAW possess strong light absorption around a broadband wavelength from 300 nm to 800 nm. As a result, the photodegradation activity test demonstrates that the HCMAW shows the degradation efficiency of 98.8% for rhodamine B (RhB) under white light irradiation for 30 min in the presence of H2O2 higher than those of HCMAS (66.3%) and commercial CuO (48.3%) under the same condition, which is one of the highest reported till date related to CuO nanomaterials for the degradation of RhB. The novel HCMAW synthesized by the ion-induced protocol is worth being generalized to more assembled hierarchical micro/nanostructures for versatile applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...