A versatile quinoxaline derivative serves as a colorimetric sensor for strongly acidic pH†
Abstract
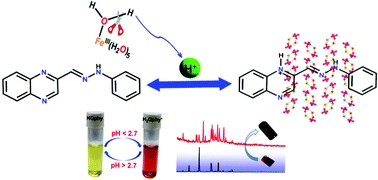
A facile and reliable method to monitor strongly acidic pH was developed. The sensing mechanism was found to involve the protonation–deprotonation equilibrium of the synthesized probe HQphy (1) (N-phenyl-N′-quinoxalin-2-ylmethylene-hydrazine) within a working range of pH 0.7–2.7. The eventual sensing of Fe3+ was the outcome of acidity imparted by [Fe(H2O)6]3+ ions in solution during the formation of [Fe(H2O)5(OH)]2+. The protonation–deprotonation phenomenon of HQphy was investigated using 1H NMR and single crystal X-ray diffraction experiments. The protonated probe, H2Qphy+, was crystallized with FeCl4−/ClO4− counter anions as [H2Qphy][FeCl4]·H2O (2)/[H2Qphy][ClO4]·H2O (3). A further complex containing the [H2Qphy] cation (4) was also formed. The complexes were characterized by SC-XRD experiments. Moreover, single crystal to single crystal transformation is observed between 1 and 3. In order to understand the sensing mechanism, various analytical studies, such as UV-Vis titration, ESI-MS spectrometry analysis and 1H NMR, were carried out in detail. A theoretical study correlates well with the experimental data, where the π(L) → π*(L) transition of the ligand is red shifted by 100 nm due to protonation of the quinoxaline moiety. The probe enables discrimination of trihalo acetic acid from its mono- and di-analogues.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...