Clean chlorination of silica surfaces by a single-site substitution approach†
Abstract
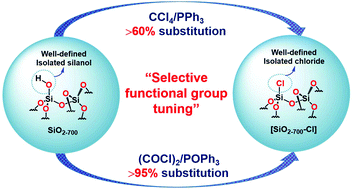
A chlorination method for the selective substitution of well-defined isolated silanol groups of the silica surface has been developed using the catalytic Appel reaction. Spectroscopic analysis, complemented by elemental microanalysis studies, reveals that a quantitative chlorination could be achieved with highly dehydroxylated silica materials that exclusively possess non-hydrogen bonded silanol groups. The employed method did not leave any carbon or phosphorus residue on the silica surface and can be regarded as a promising tool for the future functionalization of metal oxide surfaces.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...