Mechanistic insights into Pd(0)-catalyzed intermolecular and intramolecular hydroamination of methylenecyclopropanes: a computational study†
Abstract
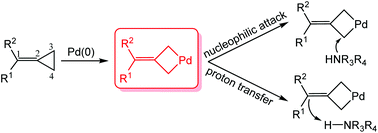
The mechanisms of transition metal-catalyzed methylenecyclopropanes (MCPs)-involved reactions are rather complicated due to the diverse pathways for the activation of MCPs. Herein, computational studies were carried out to investigate the detailed mechanisms of Pd(0)-catalyzed intermolecular and intramolecular hydroamination of MCPs. The initial activation of the three-membered ring of MCPs readily occurs via the insertion of Pd(0) into the distal C–C bond, leading to a metallacyclobutane intermediate. The commonly proposed oxidative addition of amine/amide nucleophile (Nu-H) onto the Pd(0) center to afford a hydrido-Pd(II) complex, however, is less favorable in comparison with the Pd(0)-mediated cleavage of the distal C–C bond of MCPs. Subsequently, for the Pd(0)-catalyzed intermolecular hydroamination of 1,1-diphenyl MCP with 2-pyrrolidone, it is more favorable for the C1 of the metallacyclobutane intermediate to undergo protonation to yield a π-allylpalladium intermediate, from which the final allylamine product is afforded via reductive elimination. For the Pd(0)-catalyzed intramolecular hydroamination of aniline-tethered MCP, the intramolecular nucleophilic attack of the amine moiety to C3/C4 of the corresponding metallacyclobutane intermediate is preferable to generate a cyclic intermediate. Subsequent proton transfer steps could occur to complete the hydroamination reaction. The different pKa values of the N–H bonds of amide/amine are mainly responsible for the mechanistic difference in the Pd(0)-catalyzed hydroamination of MCPs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...