Mono- and dinuclear oxidovanadium(v) complexes of an amine-bis(phenolate) ligand with bromo-peroxidase activities: synthesis, characterization, catalytic, kinetic and computational studies†
Abstract
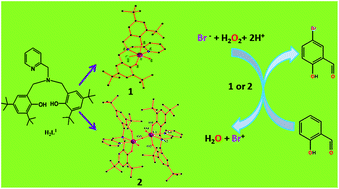
The mono- and dinuclear oxidovanadium(V) complexes [VVO(L1)(Cl)] (1) and [L1VVO(μ2-O)VO(L1)] (2) of ONNO donor amine-bis(phenolate) ligand (H2L1) were readily synthesized by the reaction between H2L1 and VCl3.(THF)3 or VO(acac)2 in MeOH or MeCN, respectively, and then characterized through mass spectroscopy, 1H-NMR and FTIR techniques. Both the complexes possess distorted octahedral geometry around each V centre. Upon the addition of 1 equivalent or more acid to a MeCN solution of complex 1, it immediately turned into the protonated form, which might be in equilibrium as: [L1ClVV![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) OH]+ ↔ [L1ClVV–OH]+ (in the case of [L1ClVV
OH]+ ↔ [L1ClVV–OH]+ (in the case of [L1ClVV![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) OH]+ oxo-O is just protonated, whereas in [L1ClVV–OH]+ it is a hydroxo species), with the shift in λmax from 610 nm to 765 nm. Similar was the case for complex 2. The complexes 1 and 2 could efficiently catalyze the oxidative bromination of salicylaldehyde in the presence of H2O2 to produce 5-bromo salicylaldehyde as the major product with TONs of 405 and 450, respectively, in the mixed solvent system (H2O : MeOH : THF = 4 : 3 : 2, v/v). The kinetic analysis of the bromide oxidation reaction indicated a first-order mechanism in the protonated peroxidovanadium complex and a bromide ion and limiting first-order mechanism on [H+]. The evaluated kBr and kH values were 5.78 ± 0.20 and 11.01 ± 0.50 M−1 s−1 for complex 1 and 6.21 ± 0.13 and 20.14 ± 0.72 M−1 s−1 for complex 2, respectively. The kinetic and thermodynamic acidities of the protonated oxido species of complexes 1 and 2 were pKa = 2.55 (2.35) and 2.16 (2.19), respectively, which were far more acidic than those reported by Pecoraro et al. for peroxido-protonation instead of oxido protonation. On the basis of the chemistry observed for these model compounds, a mechanism of halide oxidation and a detailed catalytic cycle are proposed for the vanadium haloperoxidase enzyme and these were substantiated by detailed DFT calculations.
OH]+ oxo-O is just protonated, whereas in [L1ClVV–OH]+ it is a hydroxo species), with the shift in λmax from 610 nm to 765 nm. Similar was the case for complex 2. The complexes 1 and 2 could efficiently catalyze the oxidative bromination of salicylaldehyde in the presence of H2O2 to produce 5-bromo salicylaldehyde as the major product with TONs of 405 and 450, respectively, in the mixed solvent system (H2O : MeOH : THF = 4 : 3 : 2, v/v). The kinetic analysis of the bromide oxidation reaction indicated a first-order mechanism in the protonated peroxidovanadium complex and a bromide ion and limiting first-order mechanism on [H+]. The evaluated kBr and kH values were 5.78 ± 0.20 and 11.01 ± 0.50 M−1 s−1 for complex 1 and 6.21 ± 0.13 and 20.14 ± 0.72 M−1 s−1 for complex 2, respectively. The kinetic and thermodynamic acidities of the protonated oxido species of complexes 1 and 2 were pKa = 2.55 (2.35) and 2.16 (2.19), respectively, which were far more acidic than those reported by Pecoraro et al. for peroxido-protonation instead of oxido protonation. On the basis of the chemistry observed for these model compounds, a mechanism of halide oxidation and a detailed catalytic cycle are proposed for the vanadium haloperoxidase enzyme and these were substantiated by detailed DFT calculations.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...