Liquid coordination complexes of Lewis acidic metal chlorides: Lewis acidity and insights into speciation†
Abstract
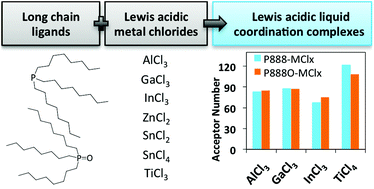
Coordination complexes of Lewis acidic metal chlorides AlCl3, GaCl3, InCl3, SbCl3, SnCl4, SnCl2, ZnCl2 and TiCl4 with trioctylphosphine (P888) and trioctylphosphine oxide (P888O) were synthesised. All compounds formed liquid coordination complexes (LCCs) at ambient temperature, although decomposition via a redox mechanism was detected in some cases. The Lewis acidity of the metal chlorides (measured in 1,2-dichloroethane solutions) and the LCCs (measured neat) was quantified by using the Gutmann acceptor number (AN) approach. In general, LCCs were equally or more Lewis acidic than the corresponding metal chlorides. The AN values were compared with the catalytic activity of selected LCCs in a model Diels–Alder reaction. Insight into speciation of LCCs was gained using multinuclear NMR spectroscopy, revealing that most LCCs comprised charge-neutral complexes rather than ionic ones. The relationship between the speciation, Lewis acidity (AN scale) and catalytic activity is discussed in detail. This approach reveals several new, promising catalytic systems, such as P888O–InCl3, with Lewis acidity enhanced compared to chloroindate ionic liquids, and P888O–TiCl4, with hydrolytic stability enhanced with respect to neat TiCl4.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...