Using an artificial tryptophan “wire” in cytochrome c peroxidase for oxidation of organic substrates†
Abstract
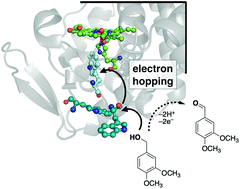
Lignolytic peroxidases use an electron transfer (ET) pathway that involves amino acid-mediated substrate oxidation at the surface of the protein rather than at an embedded heme site. In many of these peroxidases, redox catalysis takes place at a substrate accessible tyrosine or tryptophan (Trp) amino acid. Here, we describe new mutants of cytochrome c peroxidase (CcP) that were designed to incorporate a Trp-based “wire” that can move oxidizing equivalents from the heme to the protein surface. Three mutant CcP proteins were expressed and characterized: A193W, Y229W, and A193W/Y229W. These mutants can oxidize veratryl alcohol substrate with turnover numbers greater than wild type CcP using H2O2 as an oxidant. The A193W/Y229W mutant is the most active. However, the reactivity is still less than typical lignin peroxidases at pH 8. The redox reactivity of these proteins is analysed using semiclassical electron transfer theory. An electron hopping mechanism is possible for A193W/Y229W mutant. These data suggest that artificial chains of aromatic amino acids can support hole transfer from embedded sites to protein surfaces for catalytic redox reactions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...