Rapid self-healing and anion selectivity in metallosupramolecular gels assisted by fluorine–fluorine interactions†
Abstract
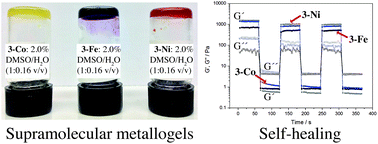
Simple ML2 [M = Fe(II), Co(II), Ni(II)] complexes obtained from a perfluoroalkylamide derivative of 4-aminophenyl-2,2′,6,2′-terpyridine spontaneously, yet anion selectively, self-assemble into gels, which manifest an unprecedented rapid gel strength recovery, viz. self-healing, and thermal rearrangement in aqueous dimethyl sulfoxide. The key factor for gelation and rheological properties emerges from the fluorine–fluorine interactions between the perfluorinated chains, as the corresponding hydrocarbon derivative did not form metallogels. The perfluoro-terpyridine ligand alone formed single crystals, while its Fe(II), Co(II) or Ni(II) complexes underwent rapid gelation leading to highly entangled fibrillar networks visualized by electron microscopy. The thermodynamic parameters of gelation based on variable temperature NMR 1H and 19F resonances showed that gelation was enthalpically favourable and entropically disfavourable. The step strain rheological experiments revealed that the gels undergo rapid self-healing and the morphological features, thermal stability and mechanical properties were found to depend on the nature of the metal ion.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 1st International Conference on Noncovalent Interactions


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...