A facile hydrothermal synthesis of carbon dots modified g-C3N4 for enhanced photocatalytic H2-evolution performance†
Abstract
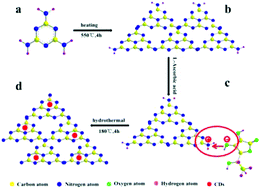
Carbon dots (CDs)/g-C3N4 is a promising photocatalyst to split water for H2 production; however, the synthesis of CDs/g-C3N4 is usually rigorous and involves multiple steps, which limits its practical application. In this study, a facile hydrothermal approach was developed to prepare CDs/g-C3N4 photocatalysts using L-ascorbic acid and g-C3N4 as the precursors. Upon in situ thermal polymerization of L-ascorbic acid on the g-C3N4 surface, the carbon dots were homogeneously and solidly modified on the g-C3N4 surface. The CDs/g-C3N4 photocatalysts showed higher photocatalytic performance for H2 production than g-C3N4 under UV light irradiation using lactic acid as the sacrificial agent. The improved photocatalytic performance of CDs/g-C3N4 was mainly attributed to rapid interfacial charge transfer. After a Pt co-catalyst was loaded, the Pt-CDs/g-C3N4 catalyst formed exhibited a further improved photocatalytic performance for H2 production and could even split pure water to produce H2. Considering our present economic and facile synthetic approach for the modification of carbon dots on the surface of g-C3N4 photocatalysts, the as-prepared CDs/g-C3N4 photocatalysts will be promising for practical use in water splitting.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...