Interactions between uranium(vi) and phosphopeptide: experimental and theoretical investigations†
Abstract
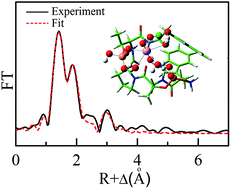
Uranium is an essential actinide element in nuclear fuel cycles, and protein phosphorylation is one type of most important post-translational modifications. It is of great interest to study the interactions between uranyl ions and phosphorylated proteins. In this study, a phosphorylated pentapeptide (WpTPpTW, P1) motif was designed as a model to mimic possible coordination sites in genuine phosphorylated proteins. Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) results suggested that uranyl–P1 complexes with chemical stoichiometry of 1 : 1 and 1 : 2 were both available. The conditional stability constant of the 1 : 1 complex uranyl–P1 was determined to be 6.6 ± 0.2 at pH 4.0 by tryptophan fluorescence titrations, which is almost three orders of magnitude higher than that of the complex of nonphosphorylated peptide. The results of extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) combined with density functional theoretical calculations suggested that uranyl ions coordinated with one phosphoryl and carboxyl groups of P1 in a mono-dentate fashion, and three water molecules. This study on the simple metal–peptide system could provide basic information for locating the uranyl coordination site in some important phosphorylated proteins which is useful for evaluating the chemical toxicity of uranyl in vivo.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...