Palladium 1D nanoscale aggregates on a graphite surface using CTAB hemicylindrical micelle templates†
Abstract
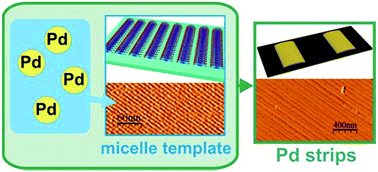
Nanoscale palladium clusters in the form of parallel strips have been formed on the surface of graphite with the help of a surface micellar template of cetyltrimethylammonium bromide using a chemical deposition method. The repeat period of the palladium strips deposited at 25 °C is 65 nm, with a width of 40 nm and height of 2 nm. The elemental composition of the metal clusters was confirmed using X-ray fluorescence analysis and TEM-EDX. The fact that the strips are composed of metallic palladium was also confirmed by testing the membrane electrode assembly with the strips in a commercial fuel cell. Using the obtained micellar template, the radius of the curvature of the AFM probe tip was estimated with the help of a unique method. The radius is equal to 10 nm and matches the value provided by the manufacturer.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...