ALD/MLD processes for Mn and Co based hybrid thin films
Abstract
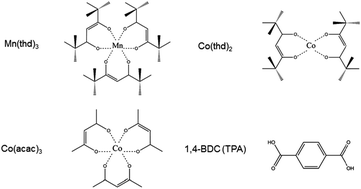
Here we report the growth of novel transition metal–organic thin-film materials consisting of manganese or cobalt as the metal component and terephthalate as the rigid organic backbone. The hybrid thin films are deposited by the currently strongly emerging atomic/molecular layer deposition (ALD/MLD) technique using the combination of a metal β-diketonate, i.e. Mn(thd)3, Co(acac)3 or Co(thd)2, and terephthalic acid (1,4-benzenedicarboxylic acid) as precursors. All the processes yield homogeneous and notably smooth amorphous metal–terephthalate hybrid thin films with growth rates of 1–2 Å per cycle. The films are stable towards humidity and withstand high temperatures up to 300 or 400 °C under an oxidative or a reductive atmosphere. The films are characterized with XRR, AFM, GIXRD, XPS and FTIR techniques.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...