Manganism and Parkinson's disease: Mn(ii) and Zn(ii) interaction with a 30-amino acid fragment†
Abstract
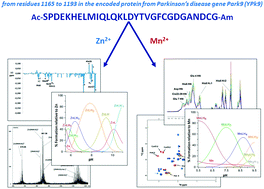
A protected 30-amino acid fragment, Acetyl-SPDEKHELMIQLQKLDYTVGFCGDGANDCG-Amide, Acetyl-Ser-Pro-Asp-Glu-Lys-His-Glu-Leu-Met-Ile-Gln-Leu-Gln-Lys-Leu-Asp-Tyr-Thr-Val-Gly-Phe-Cys-Gly-Asp-Gly-Ala-Asn-Asp-Cys-Gly-Amide, encompassing the sequence from residues 1164 to 1193 in the encoded protein from Parkinson's disease gene Park9 (YPk9), was studied for manganese and zinc binding. Manganese exposure is considered to be an environmental risk factor connected to PD and PD-like syndrome. Research into the genetic and environmental risk factors involved in disease susceptibility has recently uncovered a link existing between Park9 and manganese. It seems that manganese binding to Park9 (YPk9) protein is involved in the detoxification mechanism exerted by this protein against manganese toxicity. In this study, we used potentiometric, mono- and bi-dimensional (TOCSY, HSQC) NMR, EPR and ESI-MS measurements to analyze complex formation and metal binding sites in the peptide fragment. Presumably octahedral species, in which the Mn(II) ion was bound to oxygens of the carboxyl groups of Glu and Asp, and species where the involvement of sulfur from Cys and nitrogen from His residues, depending on the metal to ligand molar ratio, were detected for manganese coordination. Structural changes in the 30-amino acid fragment were triggered by Zn(II) interaction. A general decrease in the intensity of NMR signals was detected, suggesting the occurrence of chemical exchange among some coordinated species in an intermediate NMR timescale. The coordination may involve both S and N donor atoms from cysteine as well as histidine residues, together with O donor atoms from glutamic and aspartic residues.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...