Structural and luminescence modulation in 8-hydroxyquinolinate-based coordination polymers by varying the dicarboxylic acid†
Abstract
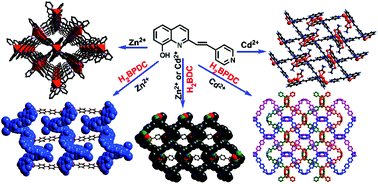
Two Zn(II) and Cd(II) coordination polymers [ZnL2·2DMF] (1) and [CdL(OAc)] (2) were first synthesized by treating a novel 2-substituted 8-hydroxyquinolinate ligand HL involving a pyridyl group with zinc or cadmium salts. Two dicarboxylic acid ligands (H2BDC = 1,4-benzenedicarboxylic acid; H2BPDC = 4,4′-biphenyldicarboxylic acid) are employed as secondary auxiliary ligands to perform a systematic study on the structural diversities in the M(II)–quinolinate frameworks. By introducing two dicarboxylate anions in the reaction system, four new polymers [Zn2L2(BDC)] (3), [Zn3L2I2(BPDC)·2MeOH·8H2O] (4), [Cd2L2(BDC)] (5) and [Cd2L2(BPDC)·2MeOH·4H2O] (6) were obtained. Complex 1 possesses a two-dimensional (2D) square grid containing meso-helical chains. Complex 2 is a 2D network fabricated by binuclear {Zn2} secondary building units (SBUs). Complexes 3 and 5 show a kind of 2D structure constructed by cyclic hexamers Zn6L4, which are divided into half by the coordinated BDC. In complex 4, the BPDC ligands bridge the 1D M(II)–L chains into a 2D layered structure. Complex 6 presents an interesting 3D structure, in which the BPDC ligands link the binuclear Cd(II) units into many meso-helical chains along the a and b axes. The diverse structures of complexes 1–6 indicate that the skeletons of dicarboxylate anions play an important role in the assembly of such different frameworks. Moreover, distinct fluorescence properties (emission wavelength and lifetime) of the complexes 1–6 were observed in the solid state.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...