Catalytic dioxygenation of flavonol by MII-complexes (M = Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu and Zn) – mimicking the MII-substituted quercetin 2,3-dioxygenase†
Abstract
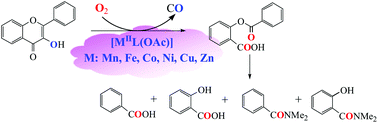
In order to get insights into the metal ion effects and the carboxylate effects on enzymatic activity, a series of the carboxylate ligand supported transition metal complexes [MIIL(OAc)] (M = Mn (1), Fe (2), Co (3), Ni (4), Cu (5) and Zn (6); LH = 2-{[bis-(pyridin-2-ylmethyl)amino]methyl}-4-methoxy benzoic acid) were synthesized and characterized as structural and functional models for the active sites of various MII-substituted resting quercetin 2,3-dioxygenases (2,3-QD). Their structures, spectroscopic features, redox properties, as well as the catalytic reactivity toward the substrate flavonol and O2 have been investigated in detail. The model complexes show higher enzymatic reactivities in the catalytic dioxygenation (oxidative ring opening) of the substrate flavonol at lower temperatures (55–100 °C), presumably caused by the carboxylate group in the supporting model ligand, which could lower the redox potential of the bound substrate flavonolate by electron donation. The catalytic reactivity of [MIIL(OAc)] exhibits notable differences and it is in a metal ion dependent order of Co (3) > Ni (4) > Zn (6) > Fe (2) > Mn (1) > Cu (5). The differences in the reactivities among them could be ascribed to the redox potential of the bound substrate flavonolate, which was drastically influenced by the metal ions via tuning the electron density of flavonolate, providing important insights into the metal ion effects and the carboxylate effects on the enzymatic activity of various MII-substituted 2,3-QD. Our model complexes [MIIL(OAc)] are the first examples of a series of structural and functional models of various MII-substituted resting 2,3-QD.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...