Lattice defects and thermoelectric properties: the case of p-type CuInTe2 chalcopyrite on introduction of zinc†
Abstract
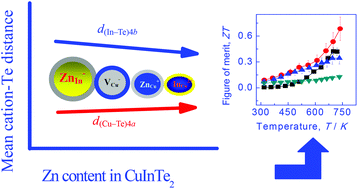
I–III–VI2 chalcopyrites have unique inherent crystal structure defects, and hence are potential candidates for thermoelectric materials. Here, we identified mixed polyanionic/polycationic site defects (ZnIn−, VCu−, InCu2+ and/or ZnCu+) upon Zn substitution for either Cu or In or both in CuInTe2, with the ZnIn− species originating from the preference of Zn for the cation 4b site. Because of the mutual reactions among these charged defects, Zn substitution in CuInTe2 alters the basic conducting mechanism, and simultaneously changes the lattice structure. The alteration of the lattice structure can be embodied in an increased anion position displacement (u) or a reduced bond length difference (Δd) between d(Cu–Te)4a and d(In–Te)4b with increasing Zn content. Because of this, the lattice distortion is diminished and the lattice thermal conductivity (κL) is enhanced. The material with simultaneous Zn substitution for both Cu and In had a low κL, thereby we attained the highest ZT value of 0.69 at 737 K, which is 1.65 times that of Zn-free CuInTe2.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...