Experimental and theoretical insights into the oxodiperoxomolybdenum-catalysed sulphide oxidation using hydrogen peroxide in ionic liquids†
Abstract
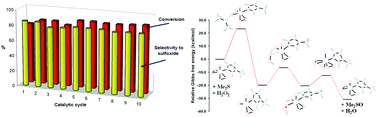
The oxidation of organic sulphides with aqueous hydrogen peroxide in ionic liquids (ILs) catalysed by oxodiperoxomolybdenum complexes was investigated. The selective formation of several sulfones was achieved using the 1 : 3 ratio of sulphide : H2O2 in [C4mim][PF6] (C4mim = 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium) in a reaction catalysed by the [Mo(O)(O2)2(H2O)n] complex. Conversely, sulfoxides were produced with good selectivities using a 1 : 1 ratio in the same solvent in a 1 h reaction with [Mo(O)(O2)2(Mepz)2] (Mepz = methylpyrazol). The use of [C4mim][PF6] as the solvent was advantageous for two reasons: (i) the improved performance of the H2O2–IL combination; (ii) recycling of the catalyst/IL mixture without a significant diminution of conversion or selectivity. A DFT analysis using the [Mo(O)(O2)2(L)] catalysts (L = Mepz, a; 3,5-dimethylpyrazole, dmpz, b; and H2O, c) indicated that a Sharpless-type outer-sphere mechanism is more probable than a Thiel-type one. The highest barrier of the catalytic profile was the oxo-transfer step, in which the nucleophilic attack of sulphide onto the peroxide ligand occurred with formation of dioxoperoxo species. In order to yield the sulfoxide and the starting catalyst, the oxidation of the resulting dioxoperoxo species with H2O2 was found to be the most favourable pathway. Subsequently, the sulfoxide to sulfone oxidation was performed through a similar mechanism involving the [Mo(O)(O2)2(L)] catalyst. The comparable energies found for the successive two oxo-transfer steps were in agreement with the experimental formation of sulfone in both the reaction with an excess of the oxidant and the stoichiometric reaction in the absence of the oxidant. In the latter case, diphenylsulfone was isolated as the major product in the 1 : 1 combination of diphenylsulphide and [Mo(O)(O2)2(Mepz)2] in the ionic liquid [C4mim][PF6]. Also, the compounds [HMepz]4[Mo8O26(Mepz)2]·2H2O, 1, [Hdmpz]4[Mo8O26(dmpz)2]·2dmpz, 2, and [Hpz]4[Mo8O22(O2)4(pz)2]·3H2O, 3, were obtained by treating in water, stoichiometrically, dimethylsulfoxide and the corresponding [Mo(O)(O2)2(L)2] complex (L = Mepz; 3,5-dimethylpyrazole, dmpz; pyrazol, pz). The crystal structures of octanuclear compounds 1–3 were indirect proof of the formation of the theoretically proposed intermediates.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...