CoMn2O4 hierarchical microspheres with high catalytic activity towards p-nitrophenol reduction†
Abstract
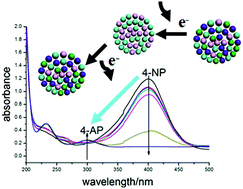
The CoMn2O4 hierarchical microspheres assembled by nanosheets through thermal decomposition of the precursor at different temperatures were first used as catalysts in the reduction of p-nitrophenol to p-aminophenol. The sample prepared at 500 °C shows the highest catalytic activity (kapp 14.95 × 10−3 s−1), which is even higher than some results reported for noble metal particles (Au, Ag and Pd). It is suggested that the presence of metal oxide with ‘d7’ (Co element) and ‘d5’ (Mn element) electronic configurations and the special morphology of CoMn2O4 hierarchical microspheres are beneficial to the reduction of p-nitrophenol to p-aminophenol.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...