Water-soluble DNA minor groove binders as potential chemotherapeutic agents: synthesis, characterization, DNA binding and cleavage, antioxidation, cytotoxicity and HSA interactions†
Abstract
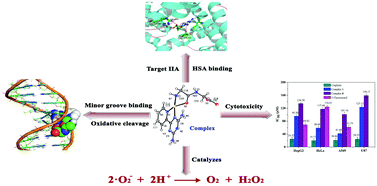
Two new water-soluble copper(II)-dipeptide complexes: [Cu(glygly)(PyTA)]ClO4·1.5H2O (1) and [Cu(glygly)(PzTA)]ClO4·1.5H2O (2) (glygly = glycylglycine anion, PyTA = 2,4-diamino-6-(2′-pyridyl)-1,3,5-triazine and PzTA = 2,4-diamino-6-(2′-pyrazino)-1,3,5-triazine), utilizing two interrelated DNA base-like ligands (PyTA and PzTA), have been synthesized and characterized. The structure elucidation for 1 performed by single crystal X-ray diffraction showed a one dimensional chain conformation in which the central copper ions arrange in a five-coordinate distorted square-pyramidal geometry. Spectroscopic titration, viscosity and electrophoresis measurements revealed that the complexes bound to DNA via an outside groove binding mode, and cleaved pBR322 DNA efficiently in the presence of ascorbate, probably via an oxidative mechanism with the involvement of ˙OH and ˙O2−. Notably, the complexes exhibited considerable in vitro cytotoxicity against four human carcinoma cell lines (HepG2, HeLa, A549 and U87) with IC50 values ranging from 41.68 to 159.17 μM, in addition to their excellent SOD mimics (IC50 ∼ 0.091 and 0.114 μM). Besides, multispectroscopic evidence suggested their HSA-binding at the cavity containing Trp-214 in subdomain IIA with moderate affinity, mainly via hydrophobic interaction. Further, the molecular docking technique utilized for ascertaining the mechanism and mode of action towards DNA and HSA theoretically verified the experimental results.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...