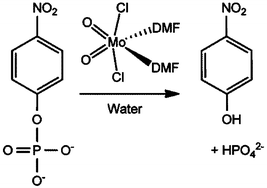
Phosphoester bond cleavage of para-nitrophenylphosphate (pNPP), a commonly used model substrate, is accelerated by using the complex MoO2Cl2(DMF)2 (1) (DMF = dimethylformamide) as a hydrolysis promoting agent, even when catalytic amounts of 1 (10 mol% relative to pNPP) are used. The reactions were performed under mild conditions (37–75 °C) and followed by 1H NMR spectroscopy. For assays performed with high amounts of 1 (1000 mol% relative to pNPP), a white solid (2) precipitates during the initial stages of the reaction, which subsequently dissolves, leading eventually to the precipitation of a less soluble yellow solid (3). Taken together, the characterization data for 2 (FT-IR spectroscopy, elemental analysis, 1H and 13C NMR, and electrospray ionization mass spectrometry) indicate that it is a polymeric material with the formula Mo2O6(DMF)n and a structure comprising infinite isopolyoxomolybdate chains built up from edge-shared {MoO6} octahedra. Compound 3 was identified as the Keggin-type phosphomolybdate [(CH3)2NH2]3PMo12O40. The formation of 3 is explained by the reaction of inorganic phosphate ions with isopolymolybdate species derived from 2, with dimethylammonium ions arising from the degradation of DMF. Both 2 and 3 are active for phosphoester bond hydrolysis with conversion profiles comparable to the ones obtained with the precursor 1.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...